Is My Website Penalized?
Join the 1,000+ brands that trust us for their link building.
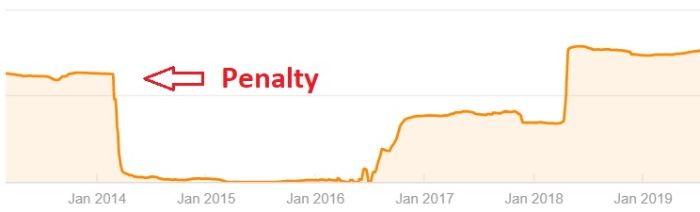
One of the worst feelings a webmaster can experience, especially when new to running a web domain, is noticing a sudden and precipitous drop in organic search traffic or ranking and having no clue why it happened.
Many people try to increase the ranking of a webpage by whatever means possible. Quite often the techniques used to boost rankings ignore the Google Webmaster Guidelines. Google is well aware of attempts to manipulate its search engine so it has developed sophisticated algorithmic filters to screen sites during indexation and remove those that violate its rules.
Sometimes websites are just poorly designed, have bad backlinks or publish bad content, and webmasters aren’t purposely trying to violate any rules. Google will penalize these sites too.
If the demotion in ranking of web pages in the SERPs is unexpected and severe, the natural reaction is to assume that your website is penalized. Many SEOs are well aware of Google’s algorithms that instruct web crawlers (i.e. bots) on how to inspect websites during indexation.
Whether you’re a webmaster, business owner, or SEO, there will come a time when you’re forced to take action in the event of one or more Google penalties. This article is here to explain what Google penalties are, what issues to check for, and how you can address them.
What is a Google penalty?
For 20 years Google has been rolling out search engine algorithms with the purpose of rewarding the SERP performance of high-quality websites and penalizing the SERP performance of low-quality sites that engage in manipulative tactics, like excessive link schemes (which may include unnatural reciprocal links) or keyword stuffing to artificially increase traffic/rankings.
Matt Cutts is the former Head of Webspam at Google. He routinely posts online videos that clarify algorithm updates and help people understand how to improve their websites to avoid penalties.
These algo updates have been released under various names like the Penguin update, Panda, Pigeon, and Hummingbird. The primary function of an update is to act as an enhanced indexation filter that screens all websites to improve search results for users, only allowing a new site that passes their guidelines to appear and rise in the SERPs.
Think of Google penalties as similar to the penalties, red flags, and suspensions in the sporting world. Most of the time these penalties are handed out to moderate the game (i.e. search engine ranking), warn players (i.e. business owners, webmasters, marketers), and offer guidance for improvement.
Google penalties are usually temporary and rarely permanent (although they can last for a long time). Even though they can cause serious damage to the performance of a website, they aren’t meant to maliciously punish people for violating rules or intimidate them from publishing websites in the future.
The quality and integrity of search results are extremely important to Google and these Google penalties exist to remind publishers and webmasters to adhere to the Google Webmaster Guidelines in order to maintain a high-quality user experience for those who use Google’s search engine to find useful information.
The Two Main Types of Penalties
A new domain needs to pass Google’s indexation filters before it stands a chance of ranking in a given SERP. It’s the job of web crawling bots to inspect every domain that’s trying to be indexed, including preexisting sites, to make sure they are following Google’s Webmaster Guidelines.
In order to make sure websites are following the high standards set forth by Google, these search engine bots are equipped with highly sophisticated algorithms that are routinely updated. These bots are responsible for dishing out automatic algorithmic penalties.
Algorithmic penalties are the most common type of action imposed on websites. They can have a very negative impact on Google ranking and traffic of affected websites. New algo updates are rolled out that update the core code of existing algos and require every site to be re-filtered based on the new rules.
On the other hand, manual penalties are manually reviewed by Google Search Advocates (real quality control employees) if they suspect foul play or if someone else has flagged your website or page to be reviewed. These manual penalties can also have a very negative impact on your ranking and traffic.
Manual penalties are directly communicated to you by email with a detailed manual action report listed in your Google Search Console. You can identify the transparent reasons for the manual penalty, its effect on your website, and the actions needed to resolve the issue.
Manual penalties are usually handed out when websites have utilized some egregious and manipulative black hat SEO tactics that violate Google’s best practices. They’re really just a second line of defense to back up the web crawlers.
On the other hand, algorithmic penalties are not reported to you through Google Search Console. Often these penalties accumulate and go unnoticed by webmasters. The only way for you to know if you’ve been slapped by an algorithmic penalty is to constantly check the health of your site (this will be explained later in the article).
Regardless of whether a site has been hit with algorithmic or manual penalties, both types will cause the affected site to lose visibility and discoverability in the search engine results. This is why rankings and organic traffic suffer when penalties occur.
Main reason you can get hit by a Google penalty
There are many specific reasons why your website or page can get hit by a Google penalty, but the overarching main reason that explains almost everything is that you’re probably trying to manipulate the search index or you’re not following the official quality guidelines for webmasters set forth by Google.
Any low-quality or unnatural aspect of your website will be flagged by Google. This includes unnatural backlinks, spam/low-quality content, and poor/deceptive optimization.
Many sites get penalized these days for aggressive and manipulative link building tactics and acquiring too many unnatural bad links in a short period of time. Although visitors aren’t affected by link schemes, this is an obvious signal to Google that someone is trying to artificially influence rankings.
There are a ton of penalties unrelated to link building. Anything that doesn’t honestly adhere to Google’s Webmaster Guidelines may warrant a penalty. For example, poor website design or irrelevant content can incur penalties.
Think of any reason that would diminish the experience of a website visitor, whether its slow loading times, spam or thin content, cloaking/sneaky redirects, or keyword stuffing, and there’s likely a Google penalty associated with it.
And there are lots of websites that don’t even realize they’ve received a penalty and do nothing to improve their situation (while their competition gains an advantage).
What happens if you get hit by one?
Several things can happen if you get hit by a Google Penalty that causes your site to get demoted due to low-quality issues or manipulative tactics:
- You lose some trust in the eyes of Google
- Your web page or website’s search ranking drops and it loses organic traffic
- You may get removed from the search index
Basically, your website or pages lose visibility in the SERPs. This almost always causes a significant decline in organic traffic (which you’ll notice in a rank checker/SEO analysis tool).
The penalty can mean a number of bad things for you and your business (if you’re running an e-commerce site). For example, your target audience can’t find your content or product page if your website is no longer indexed in search results (especially if it’s no longer in the top 10).
You’ve probably put a lot of effort into ranking for target keywords, but now you aren’t ranking for those keywords anymore.
For manual penalties, you will receive a direct notification from Google via email and Google Search Console. In this case, Google will give you a clear explanation of what happened and how it affected your website.
You’ll be given the opportunity to make necessary changes to improve your website. You will also be instructed to submit a reconsideration request after you’ve corrected your website in order to expedite the process of removing the penalty.
Algorithmic penalties just happen automatically and you’ll either notice that your web domain has been negatively affected or you won’t do anything about it. Google won’t inform you so you’ll have to proactively monitor your site.
Ways to tell if you’ve been penalized by Google
First, you need to figure out whether you’ve been hit with a manual or algorithmic penalty. Remember, you don’t receive notifications for algorithmic penalties. You only receive them for manual penalties.
Just because you haven’t received any manual penalties doesn’t mean your site hasn’t already been penalized from a string of algorithmic penalties (especially if you haven’t monitored your site with a penalty checker or analytical tool in a long time).
Algorithms, like the Penguin update, are designed to continuously check new and old websites across the web. Your site may have passed through a new index filter recently and failed some checkpoints without you knowing about it.
Manual penalties target specific websites and are always communicated through Google Search Console. Google reviewers can monitor individual websites in specific niches and also receive complaints from users who flag your site for spam, for example.
Both manual and algorithmic penalties can be sitewide (affecting the whole website) or partial (affecting one or more pages).
You should always be monitoring your website’s organic traffic and backlink acquisition. But there are several ways you can tell if you’ve been penalized or not. If you’ve received a manual action report, for example, you need to log into Google Search Console (formerly known as Webmaster Tools).
Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) is the platform that Google uses to communicate with webmasters and notify them of any manual penalties with a manual action report.
A manual penalty is when a Google Search Advocate (a real quality assurance person) notices that one or more of your web pages are violating fair practices. Sometimes a Google reviewer is informed by someone else that flags your website or page.
First, you’ll receive an email from Google about the manual penalty. Follow the link provided in the email to arrive at GSC and look at all manual action messages currently issued to your site under Manual Actions in the Security & Manual Actions tab (or go to GSC -> Search Traffic -> Manual Actions).
You can view more contextual information about each manual action through this overview such as reasons and effects on your site.
Let’s take a look at the types of manual actions you can receive.
List of Manual Actions
User-Generated Spam
Google has detected user-generated spam content on your site which may affect the ranking/indexing of the whole site or a few of its pages.
It’s pretty much what it sounds like. Visitors have posted spam comments on your site such as blog comments, forum posts, and user profiles.
This is just an example of low-quality content. You can deal with it by removing the content or user accounts. You can also provide specific guidelines to visitors to refrain from posting spam or self-promotion.
Spammy Free Host
This means a lot of sites on your free hosting service are considered spammy or filled with user-generated spam content. You can clean up your own domain but there isn’t much you can do about others.
You’ll need to contact your hosting service and inform them of the manual action or find another host so you don’t remain penalized.
Hacked Site, Cloaking, and Sneaky Redirects
Cloaking is when your site is showing different versions of webpages to users and Google crawlers to manipulate indexation and ranking. A sneaky redirect is when users are redirected to a different page that is indexed by Google.
These are deceptive tactics that violate Google’s Webmaster guidelines. Sometimes it’s not your fault and hackers have implanted scripts on your site to deceptively redirect users to other pages.
You can resolve this issue in GSC by comparing your pages with those indexed by Google. Also, keep in mind that mobile users can also be affected by sneaky redirects.
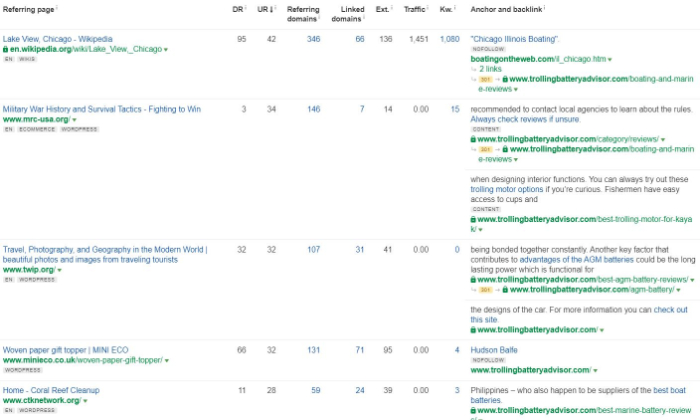
Unnatural Links To Your Site
There is a pattern of manipulative, low-quality links pointing to any page or position on your website. This is one of the big red flags to avoid when you’re trying to build an authoritative site.
The manual action for this penalty can affect your whole site or a few pages. These unnatural backlinks are usually acquired through financial transactions and artificial exchanges, or from shady niches like payday loans and adult sites.
You want to do your best to avoid these unnatural backlinks like the plague or do your best to remove and disavow them.
Unnatural links From Your Site
Just like unnatural backlinks pointing to your site, this manual action suggests a pattern of manipulative, low-quality outbound links from your website to other sites. They can originate from any position on your website.
Perform a site-wide audit and do your best to optimize or remove these bad links to avoid being penalized.
Spammy Structured Data
Your rich snippet markup is irrelevant or contains spam content. Maybe the markup is hidden from users too.
Basically, your structured markup isn’t following Google’s structured data guidelines. You can use the Structured Data Testing Tool to audit your site and resolve any issues.
Pure Spam
A pure spam manual penalty means a website has clearly violated Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and is publishing low-quality, auto-generated spam/scraped content, or using deceptive tactics to cloak indexed content.
Thin Content With No Added Value
Google has basically detected low-quality content. In other words, shallow pages with thin content, auto-generated content of little to no value, terrible guest posts, duplicate content, etc. You get the idea. Learn how to write quality blog posts.
One of the most important aspects of a high-quality website is good, relevant content. Google is always looking out for sites that meet this criteria.
You can do a quality check on your sites if necessary to remove or modify any thin or low-value content. It’s your choice to remove, edit, or replace them.
Keyword Stuffing and Hidden Text
Simply put, keyword stuffing is just placing a bunch of keywords throughout your pages that are visible to crawlers and visitors in an obvious attempt to rank higher in the SERPs. Stuffing your anchor text with keywords looks unnatural too.
Hidden text is when a website has some text that’s optimized to be seen only by Google bots and hidden from visitors in order to squeeze in more keywords to help with ranking without the web pages looking like they’re purposely being stuffed with keywords.
These tactics are considered unnatural and manipulative.

Cloaked Images
This type of penalty simply means that one or more of your site’s images are displayed differently in the search results versus how they’re displayed to visitors.
Just analyze your site and make sure every image that’s indexed by Google is identical to what website visitors will see.
AMP Content Mismatch
AMP is a web component framework for webmasters and developers to easily create websites, emails, and ads. It integrates with other tools like Google Search and Google Analytics.
This manual penalty just means that content on your “canonical” pages isn’t related to your AMP versions. The content doesn’t have to be identical, but it should be topically relevant and users should be able to accomplish similar tasks on each version.
Make sure that your canonical pages are being referenced by the correct AMP versions and that the content on both is similar and relevant.
These are some of the common manual penalties you can get. Now let’s go over algorithmic penalties.
Algorithmic slaps
Besides getting serious manual actions issued to your website from Google reviewers, more often than not your site is going to receive one or more ranking penalties over time from an algorithmic update that may go under your radar. You don’t need to log into GSC to deal with these issues because Google won’t send you a report.
Remember that Google frequently rolls out algorithm updates that crawl the web all the time to audit and re-index sites that are either following or ignoring best practices.
One of the main things algos do is count the number and quality of backlinks to determine the overall value and importance of a website. This is why we stress link diversity so much.
There also seems to be a “Sandbox Effect” whereby new sites can take quite a while to get indexed and rank in the SERPs. This is because algorithms consider a ton of factors. Domain age and the competitiveness of keywords are a couple of examples.
Some of the most common types of algorithmic slaps are link-based penalties like building unnatural links, paid auto-generated backlinks, and link spam. New rules and checkpoints are being added to algorithms all the time, so algos are becoming more efficient at detecting all kinds of policy breaches.
Having said that, algorithmic slaps are the most common type of penalty and they aren’t reported to your Google Search Console. There isn’t an option to fill out a reconsideration request and have a Google employee evaluate your site.
Instead, you need to be diligent in understanding Google’s guidelines, auditing your site completely, and correcting anything you suspect to be the cause of a drop in ranking.
Eventually, Google bots will re-index your site and you may or may not regain your original standing in the SERPs.
Check traffic
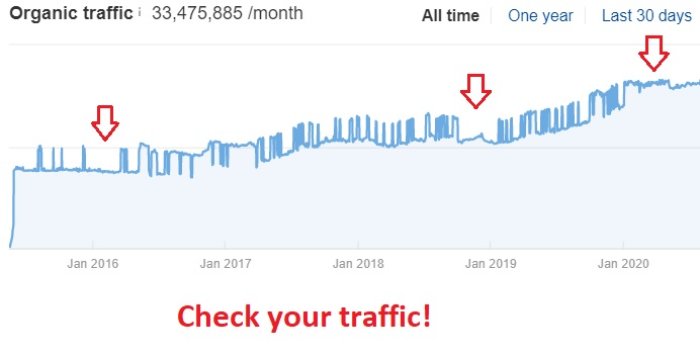
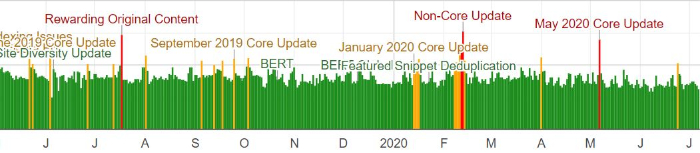
Analyzing your traffic is one of the most essential things you can do to check whether you’ve been hit with a penalty, especially if you haven’t received any manual action reports.
Keep a monthly lookout for changes in organic search traffic patterns.
This is when tools like Google Analytics, Google Penalty Checker, SEMRush, and Ahrefs come in handy. These tools give you all the analytical information you need to monitor your site’s performance over time.
You can learn more about these tools from our guide to Ahrefs alternatives.
However, a drop in traffic over time doesn’t necessarily mean your site was penalized by Google unless that drop happened suddenly or dramatically. Quite often a site’s competitors are simply gaining ground and outperforming other sites in the SERPs.
If your site’s analytics show a drop in rankings or organic traffic around a date that’s associated with the release of a new algorithm update, then your site may have been affected by the new filter. Just make sure you’re ruling out the usual traffic fluctuations like seasonality.
Sometimes your competitors are optimizing their sites to get rid of red flags and end up outranking you because of their changes, while you fall behind.
Search for you brand on Google
You should be searching for your brand on Google regardless of whether you’ve received a penalty or not.
A branded search query is when you search for a unique brand or product name (which can be in the domain name). This is particularly useful for people who’ve heard of you and want to locate your website or business.
The point is to check whether your site is ranking in the top 10 search results or not. Or if you already know where it’s been ranking, to see whether that ranking position has dropped for some reason.
You can search for the title tag text of your website to see if it’s ranking too. If nothing is showing up for your title tag or brand/product name when you think it should, you may have incurred some penalties.

How long do penalties last?
Manual penalties will eventually time out and algorithmic penalties may go away after your site is re-crawled. But keep in mind that this process can take a long time. Nobody really knows how long algorithmic penalties will last, so it’s best to address the situation as soon as possible.
There have been extreme cases of sites taking 1 or 2 years to fully recover their rankings after being slapped with algorithmic penalties (sometimes they never recover). Perhaps Google released numerous updates, and while webmasters were trying to clean up their sites during this time, they could never stay up to date with all the algo updates being rolled out.
Sometimes you can recover relatively quickly from algorithmic slaps, but you should only expect meaningful changes to occur after new updates are released or your site is re-crawled.
There is a little more clarity regarding the length of manual penalties which, depending on the seriousness of the transgression, can be a timeframe of 30 days to 6 months (or even 2 years).
Google may give you an idea of when the manual penalty should expire, but they won’t give you an exact date of when your site will begin recovering in the SERPs. If you don’t submit a reconsideration request then you can expect the maximum time frame to elapse before the manual penalty is automatically removed.
You can potentially shorten this penalty window by submitting a reconsideration request. These requests can take several days or weeks to be processed after which you will receive an email when the review is complete and whether your penalty will be lifted or not.
How to fix one
You need to take corrective action as quickly as possible after you’ve discovered that you’ve been hit with one or more penalties. If they were algorithmic, you should know whether your site is recovering or not after the next update or re-crawl.
Algorithmic slaps are more difficult to assess and correct than manual penalties because Google doesn’t send you any correspondence that explains why you received the penalty.
Fixing Algorithmic Penalties
With algorithmic penalties, you need to find some correlation between Google’s last updates, recent changes to your website, and how badly your site has been “punished” in the SERPs.
Algorithmic updates are released with general public information about what they aim to achieve or improve regarding search indexing. But you won’t know exactly which changes are relevant to your website because you won’t receive a personalized action report like you would with manual penalties.
You basically need to audit your site and make sure you change anything that you suspect of violating the Google Webmaster Guidelines or whatever is hinted in the press releases of recent algo updates.
Some algos target on-page optimization while others focus on link building and analyzing link profiles. Some algos can be very specific like making sure you’re optimizing for geolocation services.
Just do anything you can think of to improve the overall quality of your site, like analyzing your link profile, disavowing spam links, revising and improving your content, etc.
Once you’ve made substantial quality changes to your site there isn’t much you have to do but sit and wait for the next re-crawl to determine if you’ve corrected the right things.
Fixing Manual Penalties
It’s considerably more straightforward to fix manual penalties than it is to deal with algorithmic slaps.
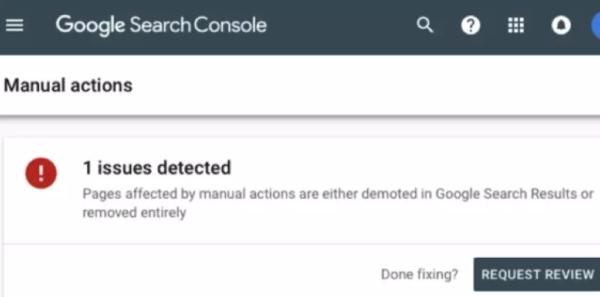
If you get a manual penalty, you or your webmaster will be notified through Google Search Console (GSC) with specific information on what’s wrong and how you can make improvements.
Through GSC you can review descriptions of the affected pages and learn how to resolve each one with detailed information and guided steps. Make sure you fix all issues on every page if you’ve received multiple penalties.
Make sure all your affected pages can easily be accessed by a Google reviewer because they’ll need to be manually assessed before you can have your penalty lifted. So make sure there are no passwords, paywalls, firewalls, noindex tags, etc.
You will request a review by submitting a reconsideration request after you’ve tackled all the issues listed in your manual action report. A good request will identify the problems, describe the specific steps you made to fix all issues, and perhaps document their outcomes.
Now you must be patient while your request is being processed and a Google reviewer checks your site to determine whether it deserves to have the penalties removed.
How to avoid getting hit by one
The best strategy is to always maintain a high-quality website that will avoid costly penalties in the first place. Penalties can cost you a lot of time, energy, and money so it’s crucial to build a quality website with great, valuable content.
Conducting SEO audits on a consistent basis is one of the best things you can do to avoid getting hit by random penalties.
There are literally hundreds or thousands of little things that Google can potentially flag and nobody expects you to identify them all. You don’t really need a perfect site to perform well in the SERPs.
Remember, your site’s performance is relative to your competition. If your niche competitors aren’t catching every single flaw with their sites then you shouldn’t have to either. Google is going to prioritize the best sites with the least flaws. No site will be completely perfect.
This article isn’t going to identify everything you need to do in order to avoid penalties, but here are suggestions on how to address the most common issues that may attract penalties:
- Remove and disavow unnatural, spammy, or shady backlinks
- Don’t allow users to post spam on your sites
- Don’t allow auto-generated content
- Publish high-quality content
- Follow on-page optimization best practices
- Remove duplicate content or spam
- Improve your UX design and decrease loading times
- Diversify your anchor text and avoid keyword stuffing
- Don’t use doorway pages
Just do your best to adhere to Google’s Webmaster Guidelines!
Conclusion
Google penalties are warnings against websites that are in conflict with the best practices and official webmaster guidelines set forth by Google.
These penalties can happen automatically in the form of algorithmic slaps, without you even knowing, or they can be directly communicated to you in the form of manual action reports.
In general, penalties are handed out when sites try to manipulate the search index with deceptive tactics that artificially increase traffic or rankings.
Manual penalties are less common these days because Google algorithms, which are constantly being updated, are becoming more efficient at identifying the clever black hat tactics that webmasters and SEOs use to manipulate search rankings (often related to link building and on-page optimization).
These algorithms are also becoming more proficient at recognizing truly quality content that adds value to website visitors, so just building quality backlinks isn’t enough these days if your site contains low-quality content.
It’s important to stay ahead of the game when it comes to optimizing your site to avoid being penalized by Google, so your website and business can continue to grow in the future. Aim to publish meaningful content that attracts natural backlinks and doesn’t give off signals that you’re trying to exploit the system.
Contributing Author: Brian Kihneman
 Article by:
Article by:
Nicholas Altimore
Hey I'm Nick, the Founder/Director here at SirLinksalot. I have a passion for building online businesses and taking websites to the next level with the help of my amazing link building team.
 Questions or Comments?
Questions or Comments?
We are active in our Facebook Group seven days a week and would love to hear from you. Ask us questions, learn from other group members, and share your knowledge.
Related Posts
Ready To Start Building Your Rankings?
Your link building journey to the top of Google starts today!
Apply for Managed Link Building to get a free analysis and game plan, or order backlinks a la carte.
Link building services that work.