Ultimate Guide To Writing Blog Posts For SEO
Join the 1,000+ brands that trust us for their link building.
It’s difficult to consistently rank well in the SERPs without publishing high-quality SEO-friendly content. Digital marketers know that SEO-friendly content is the foundation of any successful blog post and churning out compelling content on a consistent basis, that’s optimized for ranking, is key to growth no matter what niche you’re targeting.
There is nothing more frustrating than putting in the effort to make a blog post and never seeing it move up in the results pages.
You need to write SEO-friendly content in order for your hard work to pay off. SEO is the catalyst that will help your blog post rank higher in the search engine results. So you have to learn how to deliver quality blog posts that are optimized for ranking.
Having to make an SEO-friendly blog post is essential for ranking these days, but you can’t just spit out any crap and call it a day. You have to take it to the next level by implementing SEO techniques into your quality content and website/pages.
Pumping out a bunch of thin, irrelevant, and low-quality articles only puts your website at risk of being penalized by Google.
The entire process of publishing a successful blog post is actually quite simple to understand despite needing some skill and patience to learn. With practice and diligence, you’ll become proficient at delivering a high-quality post on a consistent basis.
This article will discuss the simple steps you can take to write and SEO a blog post. Some of them may seem obvious like formatting, headings, and structure. Others are more important like keyword research and keyword positioning.
Follow these 3 steps to write SEO friendly blog post:
- Keyword research (i.e. topic discovery)
- Write the content
- Perform on-page SEO for the blog post
Over time you’ll use a system that becomes good at implementing these SEO tips to write a blog post that will rank in the search engine results pages, drive traffic, and enhance your brand.
Start with Keyword Research
You need to perform research before you start writing a content piece. This activity includes discovering topics of interest within specific niches and identifying profitable keywords to rank for within those niches. You need to find out what your audience or customers are actually searching for so you can engage them and perform well on the search engine results pages.
These search terms will guide the topics you’ll write about in your SEO-friendly blog post, become the keywords to include in your content, and be the keywords you’ll optimize your web pages with. The process of ranking is nearly halfway complete after you start to write compelling content that’s related to these keywords.
Keyword research is very important and shouldn’t be rushed or performed in a haphazard manner. It’s probably the most important step in the entire process of publishing an SEO-friendly blog post and it’s really not that difficult given the amount of value it adds.
For the sake of learning, we will discuss some efficient strategies on how to rank for low competition keywords. These keywords are perfect for learning how to rank content in the search engines for targeted niches. They are relatively easy to rank for and can be quite profitable.
Low competition terms are essentially keywords that cover specific categories which aren’t being targeted by a lot of competition. They’re also associated with websites that have relatively low domain authority and low search volume. These are the characteristics that make them low competition and easier to rank for than other types of keywords (e.g. broad high-volume search terms like short tail keywords).
Our Favorite Starting Technique: Low Competition Research with Keywords Everywhere and MozBar
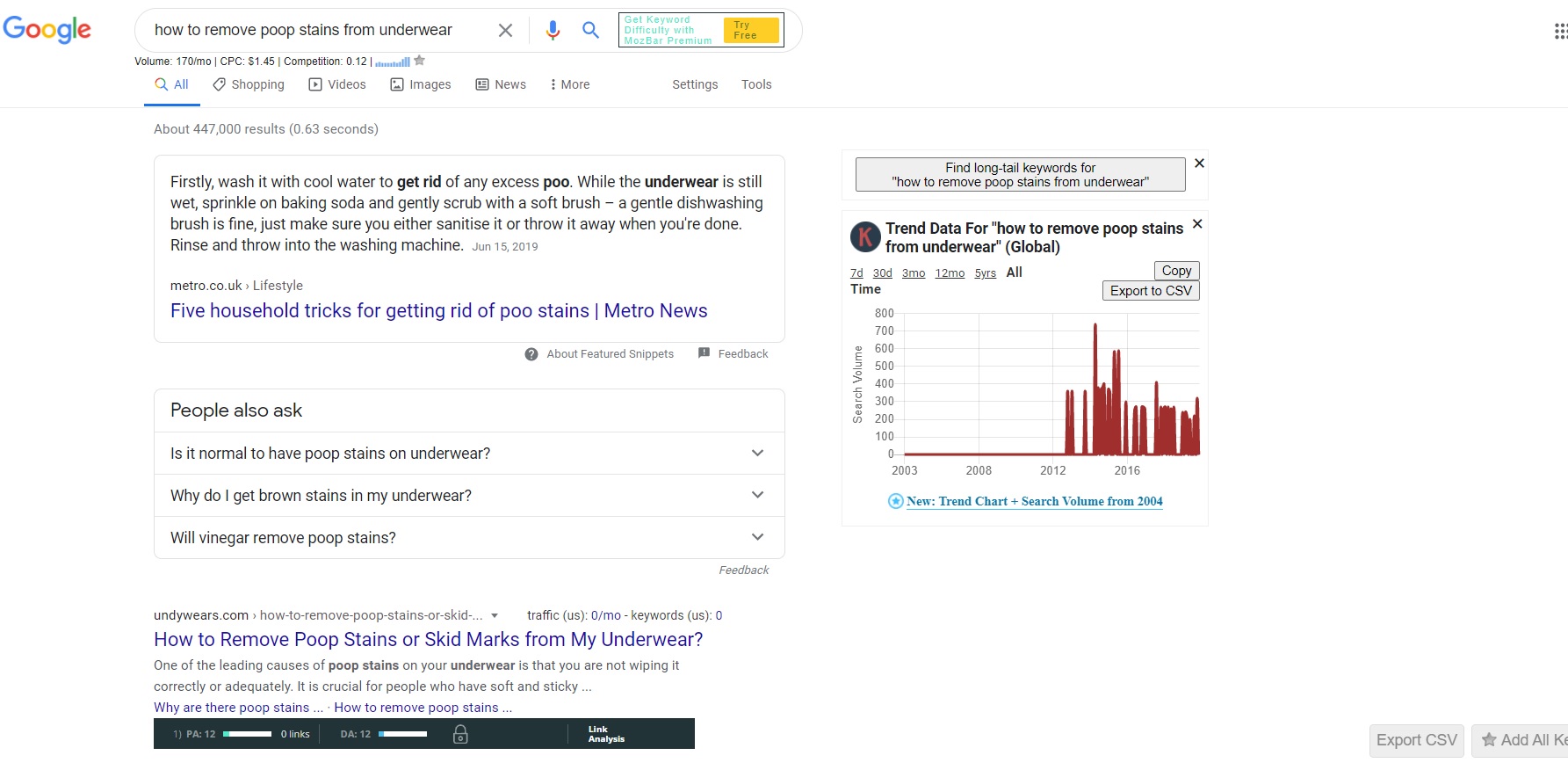
One reason why ranking for low comp keywords is quick and cheap is because you only need a couple of tools to start off successfully. The first step will be to download and install two Chrome browser plugins that are used for discovering keywords and gauging the competition: Keywords Everywhere and MozBar.
Keywords Everywhere (KE) used to be free but now offers extremely cheap plans that cost the average user about $2 a month. You purchase credits to view monthly search volume, CPC, and competition data for keywords. We use KE to look at keyword search volume and discover related search terms.
It’s easily one of my favorite SEO tools on the market, and the price can’t be beaten when you consider the ROI it helps you earn once you figure out how to use it properly.
MozBar is a free SEO toolbar for research on the go. It provides proprietary metrics for each website in a SERP. We use the tool’s domain authority metric (DA) when researching keyword ideas and gauging the level of competition in the search engine results.
In short, KE is used for search volume/related keywords and MozBar is used for domain authority (DA). These factors will help you determine the relative competitiveness of a keyword (since we are looking for low competition terms).
Finding Related Keywords and Low DA
Now it’s time to begin finding low comp keywords. It’s a good idea to start with a seed word or combination of seed words that you would personally search for to buy something. Think like a potential customer and use a buyer’s format to search. This seed keyword will be your starting point for something you’ll eventually write about.
Search for something in Google and take a look at the related keywords and suggestions given by the KE plugin on the right. Also, take a look at the results being ranked in the SERP. You will notice the MozBar toolbar below each search result with metrics for domain authority (DA) and page authority (PA). Remember, we are only concerned with the DA.
Warning – looking at Moz metrics alone is not a bulletproof sign that the SERP is going to be easy to rank for. You will need to learn how to look things over, and sometimes have to go a few levels deep examining competitor sites and their backlinks with other tools like Ahrefs in conjunction with KE and Mozbar.
Start at the top of the SERP and work your way down. Try to find websites on the first page with relatively low DA scores; the more of them on the SERP, typically the easier it is to access. As a beginner, it’s a good idea to look for the lowest DA scores you can find on a page.
A SERP with at least one or two low DA scores basically means that keyword is relatively easy to rank for (but again, relying on metrics alone is not bulletproof). Typically, this is a good sign. A SERP without a lot of high DA sites on the first page means that you don’t need a lot of authority or links to rank for that keyword.
However, some SERPs may not have any sites with a low DA score (below 40). That’s when KE is useful for discovering related keywords that may be less competitive.
You can look at the KE plugin results on the right side of the SERP to see a list of related keywords and suggestions. Some will be very similar to the initial keyword you typed in the Google search bar. Look for keywords with low search volume (100 or less) because these are the most accessible terms that indicate low competition.
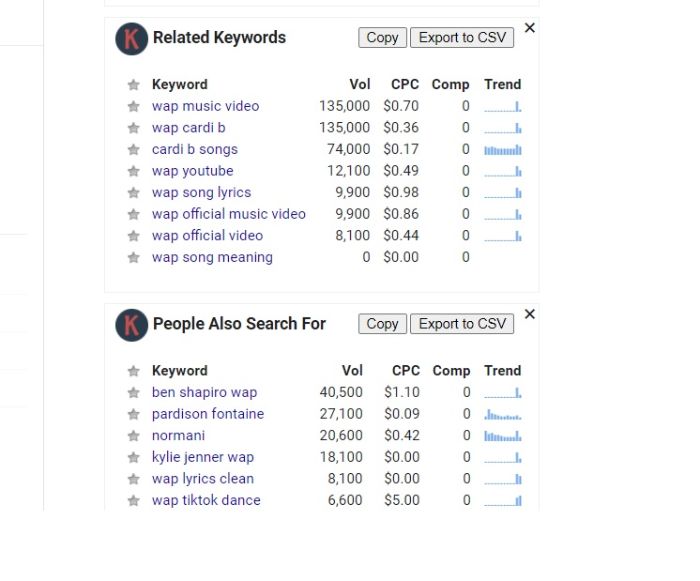
You can inspect low volume related keywords with MozBar simply by clicking the keyword link in KE to pull up its first page SERP. Then you’ll look for low DA sites the same way you did for the initial keyword. Try to identify at least one site with a low DA on the first page, as this is an indicator of relatively low competition for that keyword.
Sometimes you’ll notice sites with ultra-low DA or even 0. This doesn’t mean the keyword a site is ranking for is useless. MozBar metrics aren’t always accurate and should only be interpreted as a general gauge of competition.
This includes analyzing your own site’s power in relation to the competitors you want to beat.
You can still get good traffic (and make money) from 0 DA sites or even ultra-low search volume words. These types of keywords should be viewed as potential quick wins because they’ll take much less time and effort to rank for.
Depending on the amount of money you stand to get by converting one customer, low competition keywords can add up to be solid bankrolls over time.
The KE and MozBar strategy is an efficient way to find low competition keywords. Keep “rinsing and repeating” the process of searching for an initial keyword, looking at the authority of websites on the first page SERP, and exploring related suggestions and their SERPs.
You want to eventually narrow down your search to low competition opportunities.
Now, if you want to dive deeper into your research you should perform backlinks analysis on low DA sites that you’ve scouted with MozBar and KE. This is when Ahrefs will come in handy which we’ll briefly go over in a bit.
Before we continue with other keyword research strategies, keep in mind that this simple and effective strategy will have you ranking in no time. You will be successful at ranking if you just start out with this method and, once you join a great affiliate program or find a couple of clients, you’ll be making money too.
“Allintitle” and “Allinurl” Strategy
This strategy is more advanced than simply using KE and MozBar but it’ll allow you to dig a little deeper into the competitiveness of keywords by identifying how many search results have “allintitle” or “allinurl” SEO features.
We don’t rely on it by itself but added to the end of the aforementioned techniques it can supply you with a great indicator of easy-to-access SERPs.
Allintitle or allinurl are Google search commands that only display SERPs where a specific keyword or keyword phrase is used entirely in the SEO title or URL of a web page.
By using these commands in your search queries you’ll be able to see how many websites are optimized specifically for a keyword. It gives you a sharper picture of competition for keywords because you can see which sites are using SEO techniques to rank higher for specific terms in search engines.
This is a narrowing down process like any keyword research strategy. First, you’ll input a seed term in the Google search bar using the allintitle: or allinurl: command to return results that only have that keyword in the search engine title or URL. Lower search results generally means lower competition, so you want to narrow down your keyword choices to minimize the number of search results.
Example:
Allintitle:best seo practices
Allinurl:best seo practices
There is no space between the operator and the phrase you are researching.
Gauging competition is often a process of individual trial and error so you’ll have to determine what amount of search results you feel comfortable with. If you’re completely clueless, then keep in mind that around 1,500 “allinurl” search results is slightly competitive, so aim for less.
You want to keep getting the number of results down and finding variations of keywords with fewer pages optimizing the term in their URLs. This process will eventually arrive at low competition terms.
Reducing competition is a good way to improve performance depending on the power, authority, and relevance of your site (including its on-page and backlink profile).
So try to narrow down your keyword research to produce allinurl search results below 500. Even arriving at results below 100 can be a prime opportunity to generate easy traffic without having to buy links to boost your performance.
You can apply this technique to any amount of niches or keyword variations and expand your skill at URL and title manipulation to target SERPs other marketers aren’t looking for.
Brief Overview of Ahrefs Site Explorer
Ahrefs can be useful when you’re scouting for keywords with Keywords Everywhere (KE) and MozBar and/or using “allinurl” search commands.
You can use Ahrefs’ Site Explorer as a complementary research tool to perform backlinks analysis on competitors who are ranking for keywords of interest and to discover new keyword ideas.
First, use the KE browser extension for preliminary research ideas. Think of phrase combinations or use seed words you would type in Google to buy something. Find the top-ranked sites and use them as research inputs for Site Explorer. This is when you’ll begin reverse engineering the competition.
You don’t need to invest in expensive keyword research tools because your competitors have done a lot of the work for you, and we’ve already discussed two options that are cheap and effective.
So when you pull up the top competitors in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer you can take a look at the number of backlinks, organic keywords, and referring domains associated with their websites. This gives you a more precise picture than just using MozBar’s DA metric.
You can also look at top competitors and see if their organic keywords match your ideas and look for new ideas they are ranking for by exploring their website’s sub-niches (inner pages).
Don’t focus too much on the top-level domains (TLD) of big authority sites with thousands of links because these sites aren’t typically specializing in a low competition niche. Often these big authoritative competitors will have tens of thousands of referring domains pointing to their TLD but only a few hitting their inner pages.
It’s the inner sub-niche pages you’ll focus on to discover new low competition keyword ideas. You can build valuable niche keyword lists by exploring the inner pages of these top competitors using Site Explorer. Once again, you’re letting them do the research and discovery for you.
Start with a seed keyword in the search box, find the top-ranked sites, and reverse engineer with Ahrefs.
You can also use Ahrefs for deeper analysis when performing “allintitle” or “allinurl” searches because Ahrefs will give you competition and organic search volume data for any keyword or website. For example, Ahrefs may tell you that a keyword has 15,000 search volume and “medium competition”.
Obviously… it’s prob not very reliable as that much search volume is usually going to be closer to “very competitive”. This only stresses the importance of using more than one tool to indicate ease of getting onto a SERP.
Wrapping Up Keyword Research
Keyword research is a very important step in the process of publishing a blog post for SEO. Once you gather some good ideas you can move on to writing content and then on-page optimization.
Keyword research informs you of what your target audience is searching for and how competitive it would be to rank for specific terms in the search engines. You perform keyword research to discover new keyword ideas, narrow down opportunities, and target niche categories with relatively low search volume.
This is also your time to analyze the competition and get ideas from their websites, backlink profile, and inner pages. Often big authoritative sites have been around for a long time and have already done a lot of research for you. But they may show weaknesses in ranking for specific niche keywords that you can capitalize on.
My opinion is that the more time you spend on keyword research, the further you’ll go with the next steps. The best way to prepare a good blog post starts with intense keyword research.
From here we move on to writing relevant content that you’ll use in your blog post to rank for keywords.
Write Quality Content
The goal of writing quality blog posts is to engage your audience with compelling content, boost traffic, improve rankings, and establish a sense of trust and authority through the information that’s conveyed. This activity takes skill. Consider hiring someone if writing isn’t your strong suit or if you don’t understand the topic (or your audience).
Keep in mind that quality content is just as important as on-page optimization. They often go hand in hand because on-page SEO for a blog may include changes to the content. You’ll learn more about that after we discuss the basics of writing an SEO-friendly blog.
Writing can be really hard in general, but for some general tips and tricks you can check out this post by Writer’s Digest.
Consistently delivering useful high-quality blog posts, that are contextually relevant and evoke an emotional response, will improve organic search visibility and help generate backlinks. It sounds cliche and idealistic, but that’s simply the truth about why content is so important to SEO.
Well-written content provides an engaging experience for visitors. You have to write great content if you want to obtain high-quality links from authoritative sites (unless you’re buying them of course). People will link to articles that they like or find relevant and useful.
You can keep readers interested in your blog post by including proper structure, formatting, grammar, diction (language, keywords), catchy headings, font styles (bolding, size), spacing (short paragraphs), an introduction, logical main points, and a conclusion.
These are the elements that make any text article useful and easy to read. You want the reader to have a seamless experience from start to finish, making sure they understand what you’re trying to convey in a clean, efficient, and relevant manner.
Elements of a Quality Content Piece
The first thing you want to do when crafting a content piece, assuming you’ve already chosen a topic for the blog post, is to create an outline that establishes the structure and formatting of the content.
Structure and formatting are essential for quality articles. Structure includes the headings for the title, intro, main points, and conclusion of the blog post. All the relevant sections in your article are broken up into an organized presentation for the reader. You have to think of these elements beforehand and how you want to arrange them in your piece.
Formatting is how you want to visually display the structure and content of the blog post. This includes short paragraphs, spacing, and font styles (e.g. bolding, size). The ideal way to format your content is to divide it into small paragraphs and bold important keywords or phrases.
Keep the font style and size consistent (bigger for headings and titles) and don’t use exotic fonts. Paragraphs should average around 2.5 or 3 lines in length (shorter is okay). This makes it easier for visitors to read.
The title should include the main keyword you’re ranking for and also be concise and relevant. It should be interesting and accurately describe the content of the article. It should also be short enough that it displays in the SERPs without any breaks.
You want your headings to be catchy and relevant. You also want your introduction to engage the reader and explain why they should continue reading. The intro is where you can lead into the main body of the content. Keep the intro simple and don’t write too much.
The main body sections should always include relevant headings and short paragraphs that convey the main points. You can use formatting techniques like bullet points to further organize the information for readers.
The conclusion follows the main points and only needs to be a simple closing paragraph that reiterates a few key points. You can write about the solution to a problem, ask a new question, link to relevant sites, make comparisons, quote an authoritative figure, cite examples, etc. Just be creative and use your common sense.
Sections for feedback, comments, or related posts can be included at the end of the blog post if necessary/applicable.
Last but not least, make sure you proofread your content before publication. The actual content is your bread and butter so it shouldn’t have any glaring punctuation or grammar errors.

To summarize the process of writing quality blog posts:
- Think of the topic and write an outline first
- Formulate the structure and formatting guidelines
- Include correct headings, short paragraphs, and signal words (e.g. keywords)
- Proofread and optimize for length
- Update or add content when necessary
SEO techniques aren’t enough for ranking these days. You have to publish quality content. That means you have to put thought and effort into creating a blog post. You can’t just spit out crap and expect it to rank well.
If you really want to kick your content into high gear, we recommend using the SurferSEO content editor to optimize your content even further.
However, there is even more you can do to improve your performance after you’ve written the content. This is when on-page SEO steps in to finalize the process of writing blog posts for SEO.
Make sure you do proper onpage
We’ve already discussed half the process of publishing successful blog posts: research and writing. On-page SEO in blog post is the other much easier half that will further improve your performance in the SERPs.
On-page optimization is about enhancing your website with SEO techniques so it ranks higher and drives more organic traffic. This process is applied to the content, code, and settings of your website.
On-page does not include link building or conversion (external SEO factors). On-page SEO is about website optimization with internal factors. It includes the structuring/outlining of your content and modifying web page elements to improve ranking in search engines (this is how on-page techniques and writing content overlap each other).
We take a simple approach to on-page that focuses only on the factors that are needed for high rankings. Let’s go over these factors as succinctly as possible (this is an in-depth topic that other articles will explain in greater detail).
Keyword Positioning
By far the most important part of on-page optimization is placing your keywords (and their variations) into the website, pages, and content. This is the core aspect of on-page.
- Domain — Placing the main keyword or related keywords in the domain name (including the TLD) is the single most effective technique for on-page. Keywords in your domain tell Google what your website is about.
- Inner-Page URL — Positioning keywords in the inner-page URLs will optimize those specific pages for the keywords and is the second most important position you can place keywords.
- Title Tags (SEO Title) — Place your keyword and its variations into this position. Don’t repeat the same keyword too many times. The title tag is usually the first and only thing a user will read before clicking through (followed by the meta description).
- Heading Tags — Use these tags as headings and subheadings for the sections that organize your content. They are part of your content’s visual structure. Get keywords and their variations into these spots.
- Meta Descriptions — Metadata is displayed as the text shown below the title and URL in the search results. Meta descriptions are one of the few things a user will see and a good place to position keywords.
- Content — The content on a web page is the regular text which includes the valuable information you’re presenting to visitors. Make sure main keywords are placed in the content at least once. Don’t stuff your content with keywords because this is unnatural. Try to match the content length of your competitors and keep the keyword density at a reasonable level.
Don’t over-optimize by including the exact keyword or phrase in many of these positions (i.e. keyword stuffing). Variation is key. Remember that keyword positioning is the core aspect of on-page.
Page Speed Optimization
Page speed is how fast your web pages load for the user and is considered a ranking factor by Google. Improving page speed is good for your bounce rate because more people will stay on your website. Remember, the goal is to engage visitors and keep them reading.
- Pagespeed Insights — You can use Google’s Pagespeed Insights tool to analyze your website’s load times. It will advise you on how to make it faster if necessary.
- Image Size — Optimizing images has a big effect on improving page speed. Compress and display images at an appropriate resolution.
- Page Speed Plugins — A simple WordPress plugin that optimizes page speed may be the solution you’ll need to see drastic improvements. They specialize in advanced features like caching, CSS, and CDN support. Two great options are W3 Total Cache and WP Fastest Cache. Learn more about the best WordPress plugins here.

Image Optimization
Other than the image size changes that can quickly improve page speed, there are a few other image techniques you can apply to improve the page relevance for keywords and locations.
- Geo Tagging — Adding GPS coordinates to an image’s metadata is called geotagging. This is a useful SEO technique for local businesses that want to attract customers. It’s also useful in a social media blog post.
- A lot of SEOs are huge on geo-tagging images, personally, I don’t think much of it. If you take random samples of local sites ranking in their SERPs you will see the majority are not doing this. If it does help your rankings it’s to a minimal degree.
- Image Titles and Alt Tags (Alt text) — All images should have titles (file names) and alt text (short descriptions). Try to include your keywords in these positions. Alt text will appear if an image fails to load and also describes the image to visually impaired readers.
Schema Markup
The structured data (code) that helps communicate information about your website to search engines is called schema. Schema is responsible for a variety of features such as the featured snippets and rich snippets you notice in the SERPs.
Schema markup helps a search engine return more useful results for users. It may sound like a meta description, but it’s quite different.
You can create schema code with a schema markup generator or copy your site’s information into a template. Simple sites may have the same schema for every page. More complex sites can have different schema depending on the page type or content.
This article isn’t going to dive any deeper into this technical subject. Also, you can use schema plugins to make the process much easier.
URL Hierarchy
Imagine the URL structure as a pyramid shape with the homepage at the top and subpages/inner pages at the bottom. The homepage serves as a navigation hub that points to the website’s main categories.
Small sites may only use 1 layer in the pyramid for a few subpages. Larger sites will have multiple layers of subpages and inner pages.
Try to group your content and pages on your website in a logical manner without using too many layers in the hierarchy. You don’t want your visitors to get lost or distracted. A simple and logical structure for the pages on your website also helps Google establish page relevance.
Pages and Posts
We use pages and posts for specific reasons even though they’re basically synonymous terms.
For example, we use pages for critical elements of a website like selling products and services. We use posts for traffic-generating content that informs visitors. We like to include related keywords in our posts and link the posts to the main pages.
Linking and Anchors
Internal links and anchor text are very important for Google’s understanding of your website. Try linking to internal pages in a natural way that makes sense. This means linking pages and posts to other contextually relevant content on your website (including navigational links).
Use a variety of exact match keywords, variations, generic, and URL anchors for the anchor text. Anchor links enhance user experience and keywords positioned in anchors are noticed by web crawlers.
NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number)
Local sites should always include a company’s NAP in pages needing to rank on maps. You can place the NAP at the bottom of each page if there’s only 1 relevant address for the website. Otherwise, place a unique NAP at the bottom of the relevant landing page for a specific location.
Make sure the NAP on your site is identical to the information in the schema, profiles, directories, and local citations. You don’t want to confuse Google or customers with inconsistent NAP info.
On-Page Final Words
Remember that the core task of keyword positioning is the single most important aspect of on-page optimization. About 90% of your success will be attributed to keyword optimization.
On-page is half of the overall process of writing blog posts to rank in search engines. It’s very important and serves as the foundation for further off-page SEO and link building activities.
Smack pages like this with a couple of quality guest posts or niche edit links and you’ll be flying sky high in the SERPs.
Conclusion
It takes practice and skill to write an SEO-friendly blog post. Getting proficient at the SEO tips mentioned in this article will help you consistently deliver blog posts that rank in search engines.
Always start with keyword research before drafting an outline for a blog post. Find out what your audience and customers are searching for (don’t forget social media). Target low competition niches and gather ideas from the competition.
Write an outline that establishes the overall structure of the blog post such as the title, intro, headings, and conclusion. Identify keywords and signal words to be used in the content. Make sure your paragraphs are clear and concise. Formatting and structure are key to readability and improving the user’s experience.
A well-written and engaging article will increase traffic from search engines and generate backlinks from other sites that acknowledge the usefulness and relevance of your blog post.
Research and writing is the hardest part of writing blog posts, but on-page SEO is just as important. Keep in mind that keyword optimization is the most crucial on-page technique. But don’t overdo it by placing too many exact match keywords in all the positions (keyword stuffing).
You will be ranking in the SERPs a lot sooner than you think if you follow the steps in this article to write SEO friendly blog post. Then you can find a good affiliate program and make passive income.
Contributing Author: Brian Kihneman
 Article by:
Article by:
Nicholas Altimore
Hey I'm Nick, the Founder/Director here at SirLinksalot. I have a passion for building online businesses and taking websites to the next level with the help of my amazing link building team.
 Questions or Comments?
Questions or Comments?
We are active in our Facebook Group seven days a week and would love to hear from you. Ask us questions, learn from other group members, and share your knowledge.
Related Posts
Ready To Start Building Your Rankings?
Your link building journey to the top of Google starts today!
Apply for Managed Link Building to get a free analysis and game plan, or order backlinks a la carte.
Link building services that work.